Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants class 12

Introduction:
Flowering plants, the most diverse group of plants on Earth, employ a fascinating reproductive strategy known as sexual reproduction. This mechanism involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of seeds and the development of new plants. By understanding the intricate processes of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, we can gain insights into the remarkable evolution and diversity of these organisms.

Structure of Flowering Plants:
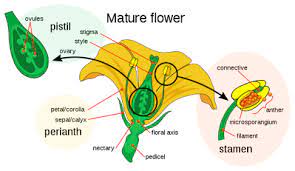
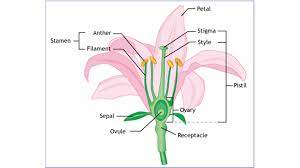
Flowering plants possess distinct reproductive structures. The male reproductive organs are housed in the stamen, which consists of the filament and the anther. The female reproductive organs are located in the pistil, comprising the stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains ovules, which serve as the site of fertilization and seed formation.

Male Reproductive Structures:
The stamen is responsible for producing and delivering pollen grains, which contain the male gametes. The anther, located at the top of the filament, contains numerous pollen sacs where pollen grains are produced. These tiny grains are essential for pollination, the transfer of pollen from the male to the female reproductive structures.
Female Reproductive Structures:
The pistil is the female reproductive organ of flowering plants. The stigma, situated at the top of the pistil, is the receptive surface for pollen grains. The style provides support for the stigma, and the ovary contains one or more ovules. The ovules house the female gametes and are crucial for fertilization and seed development.
Pollination:
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower. It can occur through various mechanisms, such as wind, water, or the activity of pollinators like bees, butterflies, birds, or bats. The process of pollination ensures the delivery of male gametes to the female reproductive structures, enabling fertilization to occur.

Fertilization:
After pollination, the pollen grain germinates on the stigma and develops a pollen tube. The pollen tube grows through the style and reaches the ovary, where fertilization takes place. Double fertilization occurs, with one sperm fertilizing the egg to form the embryo, and the other sperm uniting with polar nuclei to form endosperm, a nutritive tissue for the developing embryo.
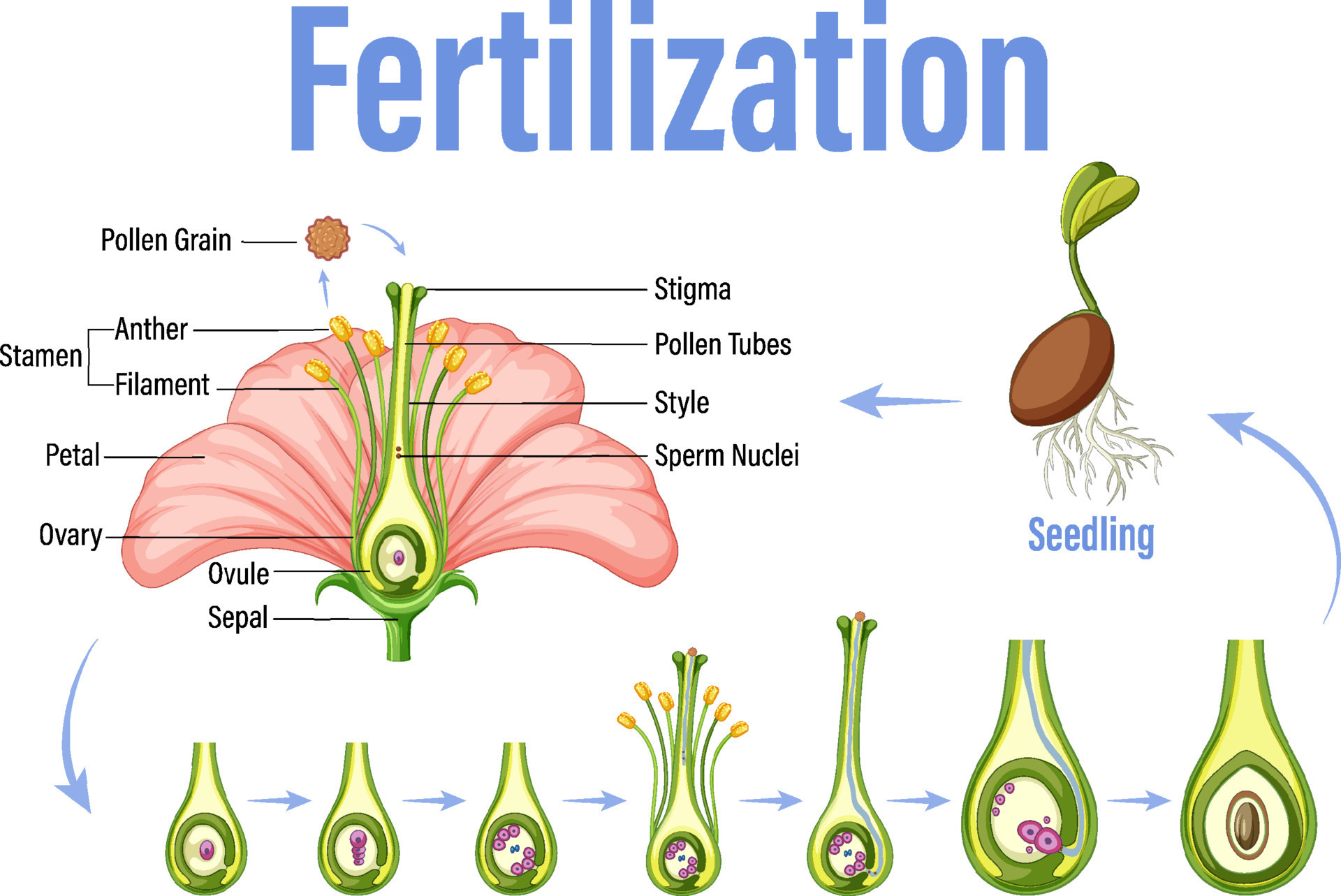
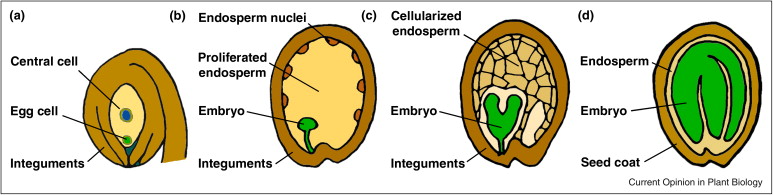
Seed Development:
Following fertilization, the fertilized ovule develops into a seed. The embryo, derived from the fertilized egg, undergoes further development within the seed. Simultaneously, the endosperm, formed by the fusion of the second sperm with polar nuclei, provides nourishment to the developing embryo. This intricate process ultimately leads to the formation of mature seeds.
Significance of Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants:
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants offers several advantages. Firstly, it promotes genetic variation by combining genetic material from two different individuals, enhancing adaptability and survival. Additionally, sexual reproduction allows for the formation of offspring with unique traits, contributing to the diversification of plant species over time.
Conclusion:
Sexual reproduction is a fundamental process in the life cycle of flowering plants. Through the fusion of male and female gametes, these plants generate seeds and ensure the continuity of their species. The intricate mechanisms of pollination, fertilization, and seed development showcase the remarkable complexity and adaptability of flowering plants.
FAQs:
-
How do flowering plants reproduce?
- Flowering plants reproduce through sexual reproduction, involving the fusion of male and female gametes.
-
What are the male reproductive structures in flowering plants?
- The male reproductive structures in flowering plants are the stamen, filament, and anther, which produce pollen grains.
-
What are the female reproductive structures in flowering plants?
- The female reproductive structures in flowering plants are the pistil, stigma, style, ovary, and ovules, which facilitate fertilization and seed development.
-
How does pollination occur in flowering plants?
- Pollination in flowering plants can occur through various mechanisms, such as wind, water, or the activity of pollinators like bees or butterflies.
-
Why is sexual reproduction important in flowering plants?
- Sexual reproduction promotes genetic variation and allows for the adaptation and evolution of flowering plant species.








